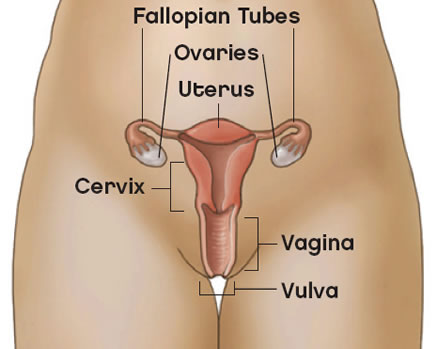
CARCINOMA VULVA
A type of cancer that occurs on the outer surface area of female genitals. Vulvar cancer is most commonly diagnosed in older women. An early diagnosis reduces the likelihood that extensive treatment will be required.
- Risks include exposure to human papillomavirus (HPV) and smoking.
- Vulvar cancer affects the external genital organs of a woman, most commonly the outer lips of the vagina.
- Symptoms include a lump, itching, and bleeding, and with some types of discoloration of the skin and pain.
- Early diagnosis increases the chance of successful treatment dramatically, but without treatment, cancer can spread to other parts of the body.
- Regularly attending smear tests and checking for changes to the vaginal lips can help diagnose vulvar cancer in the early stages.
- Avoiding smoking and unprotected sex can reduce the risk.